What is causing this loss of pigmentation?

Case 1: For several months, a 49-year-old woman has had asymptomatic loss of pigment on her shins. She has no history of injury to the area.
What is your clinical impression?
A. Vitiligo.B. Lichen planus.
C. Post-traumatic hypopigmentation.
D.Guttate hypomelanosis.
E. Tinea versicolor.
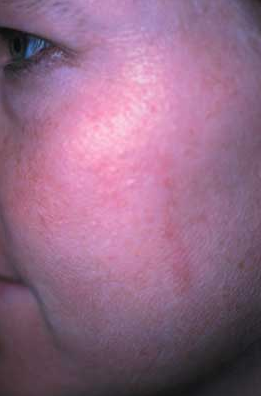
Case 2: A 45-year-old woman complains that she has had asymptomatic white “bumps” on her cheeks for the past few months.
What does this eruption look like to you?
A. Acne.B. Keratosis pilaris.
C. Milia.
D.Rosacea.
E.Sebaceous hyperplasia.
Which of the following treatments would you consider?
A. Adapalene.B.Tretinoin.
C. Tazarotene.
D.Azelaic acid.
E. Salicylic acid.

Case 3: A 68-year-old man with long-standing "arthritis" presents with an eruption on the thumb that had developed over the course of 2 years.
Which condition do you suspect is responsible for the patient's lesion?
A. Rheumatoid arthritis.B. Psoriatic arthritis.
C. Gout.
D. Osteoarthritis.
E.Calcinosis cutis.
Bonus question: True or false? Ninety-five percent of cases of this disorder occur in men.
Case 3: Tophi—nodular collections of sodium urate crystals that can rupture spontaneously-are characteristic of gout, C. The differential includes calcinosis cutis, a condition sometimes associated with connective tissue diseases and marked by deposits of calcium salts in the skin. These can occur around the fingers and erupt spontaneously. Examination of the discharged material helps distinguish gout from calcinosis cutis. Spontaneous extrusion is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or osteoarthritis.

Case 4: Hyperpigmentation developed on the face of a 35-year-old woman during her last pregnancy, but it did not resolve following childbirth.
You advise the patient to avoid excessive sun exposure and to use a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15.
Which of the following ingredients would you tell her to look for on the label of a sunscreen product?
A. Homosalate.B. Zinc oxide.
C. Methoxycinnamate.
D. Oxybenzone.
E. Butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane.
F. Octocrylene.
G.Titanium dioxide.
Bonus question: Which medication(s) can aggravate this condition?
Case 4: The patient has melasma, hyperpigmented patches that occur on the face of some pregnant women. Melasma is aggravated by UV-A light. Zinc oxide, butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane, and titanium dioxide (B, E, and G) are efficient blockers of UV-A; the others are much weaker.


